What is the Structure of an Atom? Lesson 3.1
Key Concepts
Key Terms
- What is the structure of an atom?
Key Terms
- protons
- neutrons
- electrons
- atomic number
- isotopes
- mass number
- model
Particles of Matter
- Scientists once thought that atoms were the smallest particles of matter.
- Now Scientists know more.
Atoms
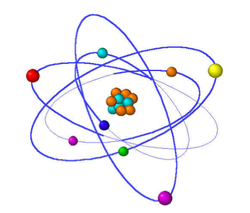
- Atoms are made of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- An atom is made up of a nucleus surrounded by one or more electrons.
Nucleus
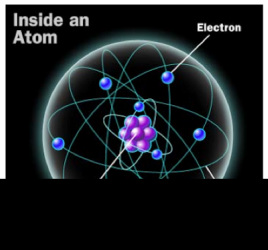
- The nucleus is the very small center core of an atom.
- It is made up of smaller particles called protons and neutrons.
Subatomic Particles
Balanced Charge
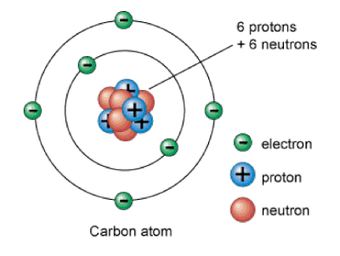
- Protons have a positive electric charge.
- Neutrons have no charge.
- Electrons move rapidly around the nucleus and have a negative electric charge.
Balanced Charge
- In an atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons.
- An atom is neutral because the positive and negative electric charges are balanced.
Electron Cloud
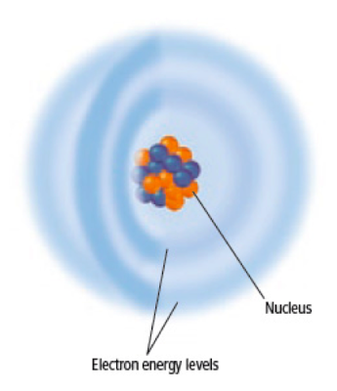
- Electrons move around the nucleus in a space shaped somewhat like a sphere.
- Scientists describe this space as a cloud of negative charge.
- Electrons may be anywhere within this cloud.

Relative Mass
- Protons and neutrons are about equal in mass.
- Electrons are much smaller.
Relative Space
- It takes almost 2,000 electrons to equal the mass of one proton.
- Electrons, however, take up much more space in the atom than does the nucleus.
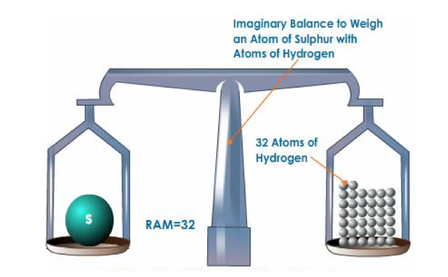
Atomic Mass Units
- Atoms are so small their masses are measured in atomic mass units (amu).
- A proton or a neutron has a mass about equal to one amu.

