How is Chemical Energy related to Chemical Change?
Lesson 1.4
Energy & Matter
Chemical Energy
- Compounds have potential energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms.
- This is a form of potential energy called chemical energy.
Chemical Change
- When a chemical change occurs, the bonds are broken and new bonds may form.
- If the chemical change is exothermic, some of the chemical energy is released in other forms like thermal energy.
Electromagnetic Energy
- Chemical changes also release a form of energy called electromagnetic energy, which travels through space as waves.
Light
- Light is one kind of electromagnetic energy.
- Other examples include radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.
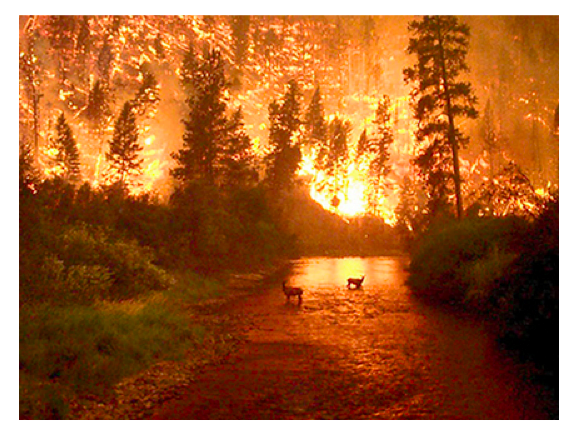
Fire
- Burning wood is a chemical change that gives off electromagnetic energy and thermal energy.
Effects of Electromagnetic Energy
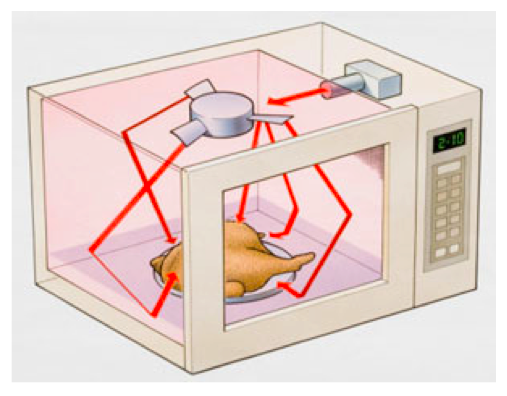
- Electromagnetic energy can also cause matter to change.
- For example, a microwave oven can change a frozen block of spaghetti and sauce into a hot meal - a physical change.
Electrical Energy
- The energy of electrically charged particles moving from one place to another is called electrical energy.
- In many chemical changes, electrons move from one atom to another.
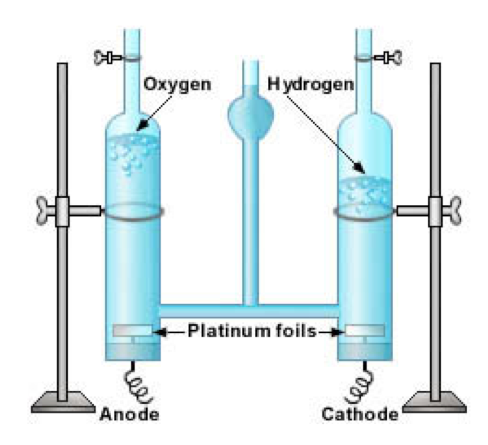
Electrolysis
- Another chemical change, electrolysis, involves electrical energy.
- In electrolysis, two metal strips called electrodes are placed in a solution.
Chemical Energy
- Every time matter changes, energy is involved.
- During a chemical change, chemical energy may be changed to other forms of energy.
Converting to Chemical Energy
- Other forms of energy may also be changed to chemical energy.
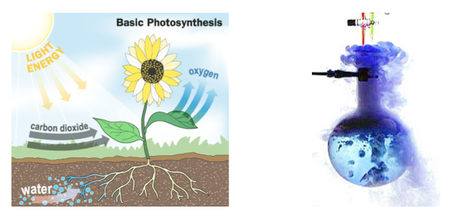
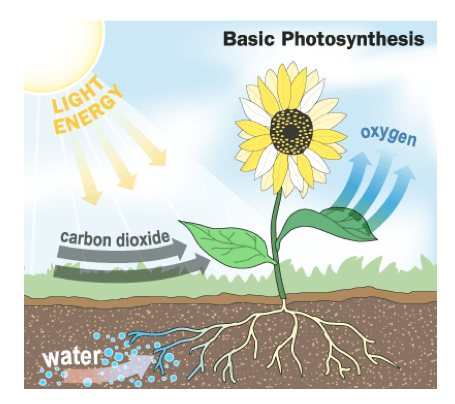
- One important example of energy change is photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
- In photosynthesis, plants change electromagnetic energy from the sun into chemical energy as they make sugar.
Energy for Life
- These plants, as well as the animals that eat them, change this chemical energy into energy needed for life activities.